How Your Credit Score For Best Mortgage Rates Affects Refinancing And How To Improve It
Refinancing your mortgage can be a smart way to save money and potentially shorten your loan term. But did you know that your credit score is the single biggest factor that determines the interest rate you’ll qualify for? This article will guide you through understanding how your credit score impacts your refinancing options, explore strategies to improve your credit score for best mortgage rates, and outline other factors that lenders consider.
Understanding the Credit Score for Best Mortgage Rates: Why It Matters
Credit Scores and Mortgage Rates: A Direct Relationship
The correlation between credit scores and interest rates is clear: the higher your score, the lower your interest rate. Lenders use credit scores to assess the risk of lending to you, which directly influences the interest rates they offer. As of August 2024, borrowers with a FICO score ranging from 760 to 850 can expect interest rates around 3.408%. In contrast, those with scores between 700 and 759 may see rates closer to 3.63%. Meanwhile, borrowers with credit scores in the 620-639 range could face rates as high as 4.997%.
The disparity in rates can lead to significant savings over the life of your loan. For example, a borrower with a $300,000 mortgage at 3.408% would pay approximately $1,328 monthly, while a borrower with a 4.997% rate would pay about $1,600 monthly—resulting in a difference of over $300 each month and more than $100,000 in interest payments over 30 years.
FICO Scores: The Industry Standard
When it comes to refinancing, the FICO score is the gold standard. Lenders heavily rely on this metric to evaluate your creditworthiness and determine your refinancing terms. While other scoring models, such as VantageScore, exist, they do not carry the same weight in the mortgage industry. It’s crucial to understand that different lenders might use varying versions of the FICO score, which can affect your eligibility and loan terms. Therefore, checking your FICO score before initiating the refinancing process is essential to ensuring you know where you stand.
Understanding Credit Score Ranges and Their Implications
Your credit score falls within a range that reflects your creditworthiness. According to the Fair Isaac Corporation (FICO), these ranges are:
- Exceptional: 800 or higher
- Very Good: 740 to 799
- Good: 670 to 739
- Fair: 580 to 669
- Poor: 579 or lower
Each category has implications for your refinancing options. Scores above 740 typically allow access to the best rates, while those below 620 may struggle to secure refinancing altogether. Understanding where you stand in this spectrum can help you strategize your path toward better refinancing terms.
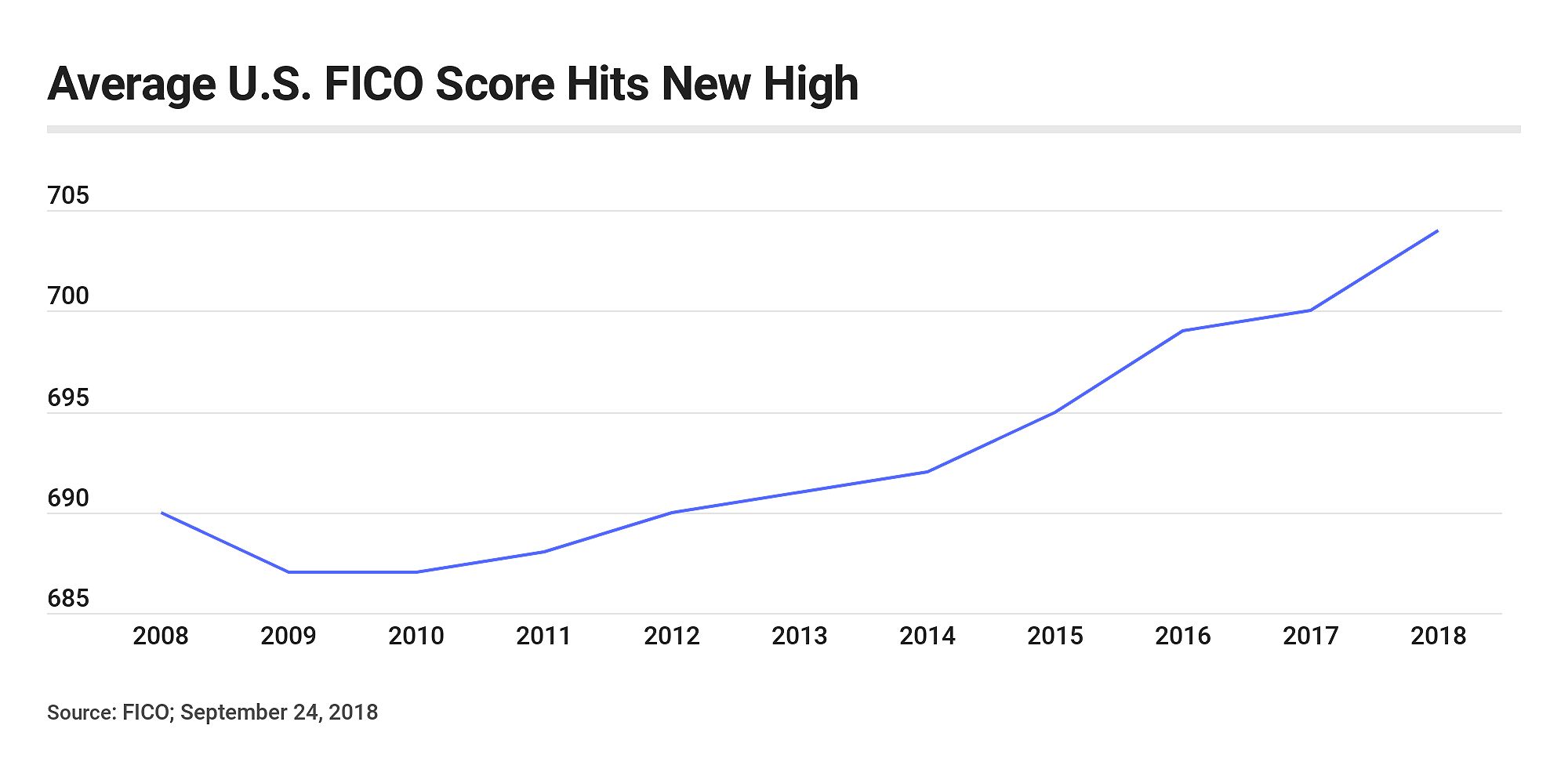
Improving Your Credit Score for Better Refinance Terms
Payment History: The Foundation of a Strong Credit Profile
Your payment history is the most significant factor influencing your credit score. Consistently making on-time payments is crucial for maintaining a strong credit profile. A single missed payment can have a lasting negative impact on your score. To avoid this, consider setting up automatic payments or reminders to ensure you never miss a due date. Additionally, it’s essential to pay all bills on time, including credit cards, loans, and utilities, as they all contribute to your overall creditworthiness.
Credit Utilization: Managing Your Available Credit Wisely
Credit utilization—the ratio of your current credit balances to your total credit limits—plays a vital role in your credit score. Experts recommend keeping this ratio below 30% to maximize your score. For instance, if your credit card limit is $10,000, aim to maintain a balance of no more than $3,000. This not only positively impacts your credit score but also demonstrates responsible credit management to lenders. Consider strategies like paying down existing balances or requesting higher credit limits to help lower your utilization ratio.
Debt Management: Strategies for Reducing Your Financial Burden
Managing existing debt effectively is essential for improving your credit score. High-interest debt can hinder your refinancing options, so consider strategies such as debt consolidation or balance transfers. For instance, if you have credit card debt with high-interest rates, transferring the balance to a lower-interest card can save you money. Additionally, creating a debt repayment plan can help prioritize high-interest debts and accelerate your journey toward financial stability.
New Credit Applications: Avoid Unnecessary Score Impacts
If you plan to refinance, it’s wise to minimize new credit applications. Each application results in a hard inquiry, which can temporarily decrease your credit score. Avoid applying for new credit cards or loans until after your mortgage has been approved. This strategy helps maintain a stable credit profile and presents you as a low-risk borrower to lenders.
Beyond Credit Score: Other Factors Influencing Refinancing Approval
While your credit score is paramount, lenders consider various other factors when evaluating your refinancing application. Understanding these factors can provide you with a more comprehensive view of your refinancing eligibility.
Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): Balancing Your Income and Expenses
Your debt-to-income ratio compares your monthly debt payments to your gross monthly income. Lenders typically prefer a DTI below 36% for the best refinancing terms. A lower DTI indicates that you have a manageable level of debt relative to your income, making you a more attractive candidate for refinancing. If your DTI is high, consider strategies to lower it, such as paying down debts or increasing your income through additional work or a raise.
Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV): Your Equity Position in Your Home
The loan-to-value ratio measures the amount of your mortgage compared to your home’s value. A lower LTV, ideally below 80%, can lead to more favorable refinancing conditions. If your home has appreciated in value since you purchased it, your LTV may have improved, qualifying you for better rates. To enhance your LTV, focus on paying down your mortgage balance or consider increasing your home’s value through renovations or improvements.
Employment and Income History: Demonstrating Financial Stability
Lenders seek stability in your employment and income history, as this reassures them of your ability to make mortgage payments consistently. A long tenure with the same employer or a steady income stream can work in your favor. If you’ve recently changed jobs or experienced income fluctuations, be prepared to provide documentation that explains these changes and demonstrates your financial stability.
Property Value: Unlocking Equity for Refinancing
The value of your home is a critical consideration for lenders, as it directly impacts the amount you can borrow and the terms of your refinance. If you believe your home has increased in value, consider obtaining a professional appraisal before applying for refinancing. A recent appraisal can help secure a better loan amount and more favorable interest rates.
Exploring Refinancing Options with a Lower Credit Score
If your credit score is on the lower end, refinancing may seem daunting, but options are available. This section explores alternative pathways for those facing credit challenges.
Government-Backed Loans: Expanding Access to Refinancing
Government-backed loans, such as those offered by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), can provide more lenient credit score requirements. For example, FHA loans accept borrowers with scores as low as 580, while VA loans may not have a minimum score requirement at all. These options can offer a lifeline for borrowers struggling with lower credit scores.
Co-Signers: Leveraging Stronger Credit for Refinancing
Utilizing a co-signer with a stronger credit profile can enhance your chances of securing a refinance, even if your credit score is less than ideal. A co-signer agrees to take responsibility for the loan if you default, which can reassure lenders and potentially result in better terms for your refinance. However, both parties should understand the responsibilities and risks involved in this arrangement.
Credit Repair: Addressing Credit Issues for Improved Refinancing
Working with a credit repair service can help you tackle errors or negative items on your credit report, potentially boosting your score and opening up more refinancing opportunities. These services can guide you through disputing inaccuracies and provide strategies for improving your credit profile over time.
Waiting to Refinance: A Strategic Approach to Credit Improvement
If feasible, consider postponing your refinance plans until you can improve your credit score. A higher credit score can lead to substantial savings over the life of your loan. Take the time to implement credit improvement strategies, such as reducing debt and ensuring timely payments, before proceeding with refinancing.
FAQ
Q: How long does it take to improve my credit score?
A: The time it takes to improve your credit score varies, but it typically requires several months of responsible credit behavior to see a noticeable increase. Factors such as payment history, credit utilization, and the age of your credit accounts all play significant roles.
Q: What is a good credit score for refinancing?
A: Generally, a credit score of 740 or higher is considered excellent for refinancing, allowing you to qualify for the best interest rates and terms. However, scores as low as 620 may still be eligible for certain loan programs, albeit with higher rates and fees.
Q: Can I refinance if I have a recent late payment?
A: A recent late payment can complicate your refinancing efforts, as lenders view this as an increased risk. However, it’s not an absolute barrier. If you can demonstrate that the late payment was an isolated incident and your overall payment history is strong, you may still secure a favorable refinance.
Q: What are the best ways to lower my debt-to-income ratio?
A: Effective strategies for lowering your debt-to-income ratio include paying down outstanding debts, increasing your income through a raise or additional employment, and avoiding new loans or credit card balances.
Q: What are the benefits of refinancing my mortgage?
A: Refinancing your mortgage can offer numerous advantages, including the opportunity to secure a lower interest rate, reduce your monthly payments, shorten the loan term, or tap into your home’s equity for home improvements or other financial needs.
Conclusion: Unlocking Your Best Refinancing Options
In conclusion, understanding how your credit score for best mortgage rates influences your refinancing opportunities is crucial for any homeowner. By taking proactive steps to improve your credit profile and understanding the additional factors that lenders consider, you can position yourself for better refinancing terms and significant savings. Don’t hesitate to check your credit score, explore refinancing options, or contact a mortgage professional for guidance on your journey toward achieving your financial goals.
MORE FROM pulsefusion.org